Cardio vs. Conditioning

Cardio vs. Conditioning. These two words are generally used interchangeably, but there is a significant difference between the two that may be holding you back from reaching your fitness and/or body composition goals.
Cardio Fitness, which is associated with general fitness, is used to maintain good health and overall well-being. There is no training goal in mind and the focus is on quality-of-life general health. Some examples include swimming, group fitness, riding a stationary bike, and walking.
Conditioning is either performance-based or body-composition focused and generally associated with athlete performance. Performance-based conditioning is used to optimize performance related to physical fitness tests, sports, and competition. Some examples include running faster, biking longer, responding to unpredictable demands quickly, agility drills, plyometrics, conditioning circuits, sleds, and Semper Fit HITT classes. This type of training is ideal for zones 3-5. Body-composition focus is used to decrease or maintain body fat percentage and weight. This can be longer duration, but less intense. Some examples include a 3-mile run at a slower pace, intervals of 30-seconds fast/1-minute slow, which is then repeated. This type of training is ideal for zones 2-4.
How To Choose A Training Zone:
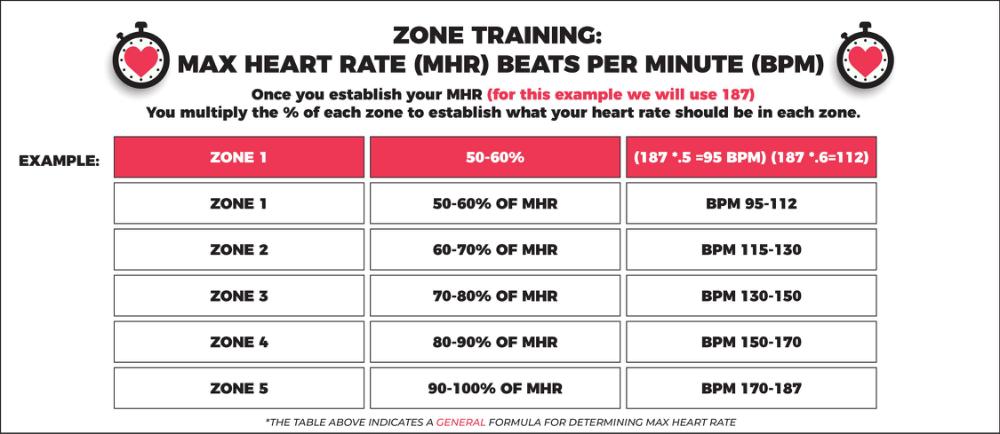
Step 1: Find your Max Heart Rate (MHR) by subtracting 220 from your age. 220-Age=Max Heart Rate (MHR).
Example: 220-33(age)=187(MHR)
Step 2: Use the MHR to figure out your Training Zone Heart Rate.
Step 3: Multiply your MHR by the percentage in the training zone chart below to find your Heart Rate Range (HRR).
Step 4: Use your MHR to find your different zones.
If wanting to increase performance in a specific task, such as running or biking, you should do that for conditioning. If it is for general fitness or burning calories, pick any exercise and track your heart rate.
Training Zone Key
Zone 1: Warm-Up & Recovery
Low intensity is used during warmups and cool-downs post-training. Zone 1 can be used for active recovery.
Zone 2: General Endurance & Fat Burning
Burns fat as a primary fuel source. Should be able to sustain this zone for extended periods of time. Increase general endurance. Zone 2 is the best place to start training programs at. Can also be used for active recovery.
Zone 3: Aerobic Fitness
Increases efficiency of heart pumping blood to working muscles. When enhanced, allows you to recover faster from harder training sessions.
Zone 4: Anaerobic Fitness
Increases lactate threshold (the time when your body burns, and you must stop exercising – think Combat Fitness Test (CFT)). Zone 4 also increases weightlifting performance.
Zone 5: Max Effort
This zone is where you increase max speed and other maximal capacities. Zone 5 cannot be maintained for extended periods of time. Increases in this zone will enhance max speed, max strength, and explosiveness.
For a sample conditioning program, visit usmc-mccs.org/articles/base-building-conditioning-protocol/.
To learn more about cardio and conditioning, visit your installations fitness center and speak with a Semper Fit Trainer or Strength and Conditioning Coach.
For additional resources, visit the following: